A Complete Guide to Fluoropolymers
Comments Off on A Complete Guide to FluoropolymersWhat Is a Fluoropolymer?
The high-performance fluoropolymer plastic family is known for its strong carbon-fluorine bonds. Fluoropolymers offer chemical resistance, electrical insulation, and thermal stability, making them ideal for many industrial uses. Some of these include medical, automotive, electronics, and aerospace applications. They come in several types: PTFE, ETFE, PFA, CTFE, PVDF, ECTFE, FEP, Rulon®, and PCTFE. Here, we will explore what fluoropolymers are and the properties of each type to help you choose the ideal solution for your application.
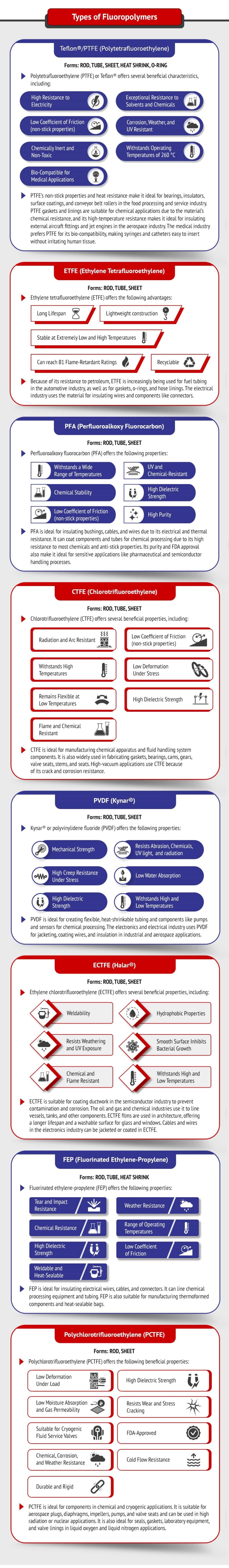
Types of Fluoropolymers
Teflon®/PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene)
Forms: ROD, TUBE, SHEET, HEAT SHRINK, O-RING
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) or Teflon® offers several beneficial characteristics, including:
- High resistance to electricity
- Low coefficient of friction (non-stick properties)
- Chemically inert and non-toxic
- Bio-compatible for medical applications
- Exceptional resistance to solvents and chemicals
- Corrosion, weather, and UV resistant
- Withstands operating temperatures of 260 °C
PTFE’s non-stick properties and heat resistance make it ideal for bearings, insulators, surface coatings, and conveyor belt rollers in the food processing and service industry. PTFE gaskets and linings are suitable for chemical applications due to the material’s chemical resistance, and its high-temperature resistance makes it ideal for insulating external aircraft fittings and jet engines in the aerospace industry. The medical industry prefers PTFE for its bio-compatibility, making syringes and catheters easy to insert without irritating human tissue.
ETFE (Ethylene Tetrafluoroethylene)
Forms: ROD, TUBE, SHEET
Ethylene tetrafluoroethylene (ETFE) offers the following advantages:
- Long lifespan
- Lightweight construction
- Stable at extremely low and high temperatures
- Can reach B1 flame-retardant ratings
- Recyclable
Because of its resistance to petroleum, ETFE is increasingly being used for fuel tubing in the automotive industry, as well as for gaskets, o-rings, and hose linings. The electrical industry uses the material for insulating wires and components like connectors.
PFA (Perfluoroalkoxy Fluorocarbon)
Forms: ROD, TUBE, SHEET
Perfluoroalkoxy fluorocarbon (PFA) offers the following properties:
- Withstands a wide range of temperatures
- Chemical stability
- Low coefficient of friction (non-stick properties)
- UV and chemical resistant
- High dielectric strength
- High purity
PFA is ideal for insulating bushings, cables, and wires due to its electrical and thermal resistance. It can coat components and tubes for chemical processing due to its high resistance to most chemicals and anti-stick properties. Its purity and FDA approval also make it ideal for sensitive applications like pharmaceutical and semiconductor handling processes.
CTFE (Chlorotrifluoroethylene)
Forms: ROD, TUBE, SHEET
Chlorotrifluoroethylene (CTFE) offers several beneficial properties, including:
- Radiation and arc resistant
- Low coefficient of friction (non-stick properties)
- Withstands high temperatures
- Low deformation under stress
- Remains flexible at low temperatures
- High dielectric strength
- Flame and chemical resistant
CTFE is ideal for manufacturing chemical apparatus and fluid handling system components. It is also widely used in fabricating gaskets, bearings, cams, gears, valve seats, stems, and seats. High-vacuum applications use CTFE because of its crack and corrosion resistance.
PVDF (Kynar®)
Forms: ROD, TUBE, SHEET
Kynar® or polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) offers the following properties:
- Mechanical strength
- Resists abrasion, chemicals, UV light, and radiation
- High creep resistance under stress
- Low water absorption
- High dielectric strength
- Withstands high and low temperatures
PVDF is ideal for creating flexible, heat-shrinkable tubing and components like pumps and sensors for chemical processing. The electronics and electrical industry uses PVDF for jacketing, coating wires, and insulation in industrial and aerospace applications.
ECTFE (Halar®)
Forms: ROD, TUBE, SHEET
Ethylene chlorotrifluoroethylene (ECTFE) offers several beneficial properties, including:
- Weldability
- Hydrophobic properties
- Resists weathering and UV exposure
- Smooth surface inhibits bacterial growth
- Chemical and flame resistant
- Withstands high and low temperatures
ECTFE is suitable for coating ductwork in the semiconductor industry to prevent contamination and corrosion. The oil and gas and chemical industries use it to line vessels, tanks, and other components. ECTFE films are used in architecture, offering a longer lifespan and a washable surface for glass and windows. Cables and wires in the electronics industry can be jacketed or coated in ECTFE.
FEP (Fluorinated Ethylene-Propylene)
Forms: ROD, TUBE, HEAT SHRINK
Fluorinated ethylene-propylene (FEP) offers the following properties:
- Tear and impact resistance
- Weather resistance
- Chemical resistance
- Range of operating temperatures
- High dielectric strength
- Low coefficient of friction
- Weldable and heat-sealable
FEP is ideal for insulating electrical wires, cables, and connectors. It can line chemical processing equipment and tubing. FEP is also suitable for manufacturing thermoformed components and heat-sealable bags.
Rulon®
Forms: ROD, TUBE, SHEET
Rulon® offers the following properties:
- Low coefficient of friction
- Resistant to chemicals
- Abrasion resistance for improved lifespan
- Withstands a range of temperatures and pressures
Rulon® is ideal for manufacturing piston rings, seals, thrust and flanged bearings, sleeves, skived sheets, bearings, and other components for valves, appliances, air compressors, and printers.
Polychlorotrifluoroethylene (PCTFE)
Forms: ROD, SHEET
Polychlorotrifluoroethylene (PCTFE) offers the following beneficial properties:
- Low deformation under load
- High dielectric strength
- Low moisture absorption and gas permeability
- Resists wear and stress cracking
- Suitable for cryogenic fluid service valves
- FDA-approved
- Chemical, corrosion, and weather resistance
- Cold flow resistance
- Durable and rigid
PCTFE is ideal for components in chemical and cryogenic applications. It is suitable for aerospace plugs, diaphragms, impellers, pumps, and valve seats and can be used in high radiation or nuclear applications. It is also ideal for seals, gaskets, laboratory equipment, and valve linings in liquid oxygen and liquid nitrogen applications.
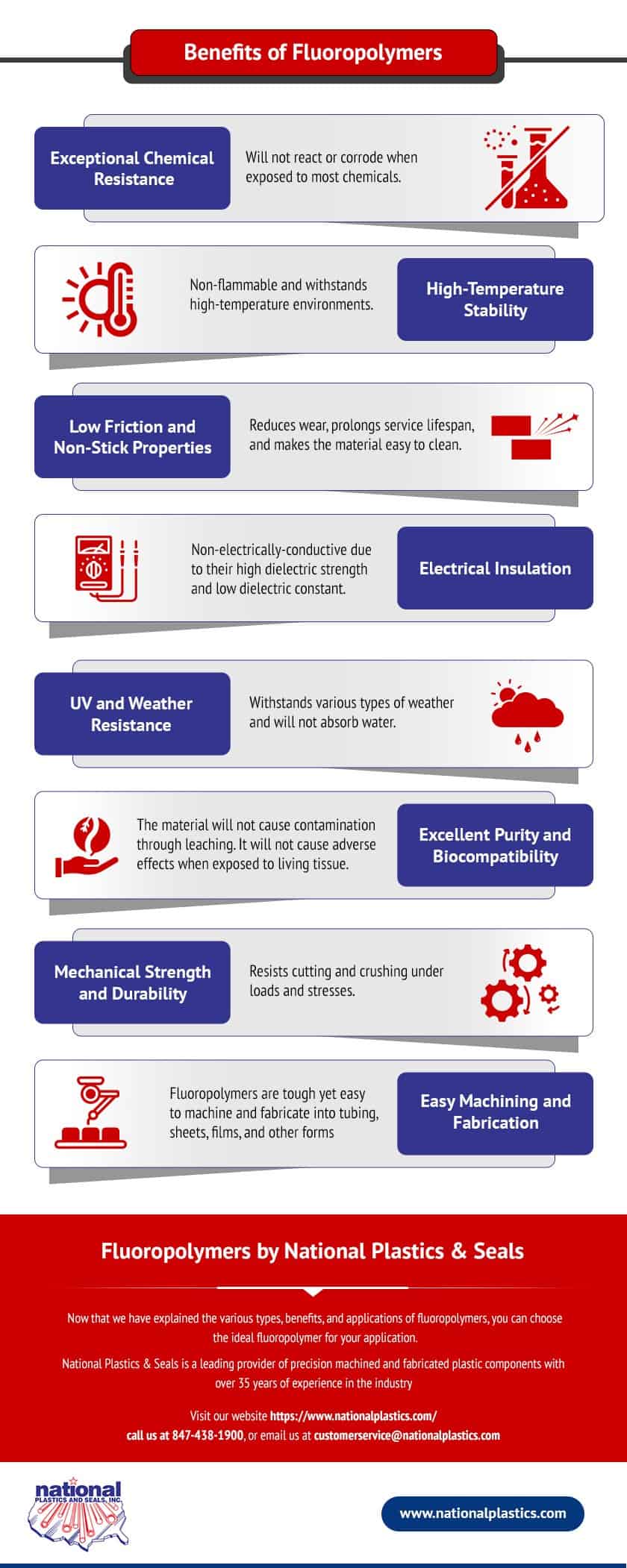
Benefits of Fluoropolymers
Fluoropolymers are a preferred material in various applications and industries due to their favorable properties:
- Exceptional Chemical Resistance: Will not react or corrode when exposed to most chemicals.
- High-Temperature Stability: Non-flammable and withstands high-temperature environments.
- Low Friction and Non-Stick Properties: Reduces wear, prolongs service lifespan, and makes the material easy to clean.
- Electrical Insulation: Non-electrically-conductive due to their high dielectric strength and low dielectric constant.
- UV and Weather Resistance: Withstands various types of weather and will not absorb water.
- Excellent Purity and Biocompatibility: The material will not cause contamination through leaching. It will not cause adverse effects when exposed to living tissue.
- Mechanical Strength and Durability: Resists cutting and crushing under loads and stresses.
- Easy Machining and Fabrication: Fluoropolymers are tough yet easy to machine and fabricate into tubing, sheets, films, and other forms.
Fluoropolymers by National Plastics & Seals
Now that we have explained the various types, benefits, and applications of fluoropolymers, you can choose the ideal fluoropolymer for your application. National Plastics & Seals is a leading provider of precision machined and fabricated plastic components with over 35 years of experience in the industry. Request a quote to start a solution for your application.